Web-based protocol handlers
Background
It's fairly common to find web pages link to resources using non-http protocols. An example is the mailto: protocol:
html
<a href="mailto:webmaster@example.com">Web Master</a>
Web authors can use a mailto: link when they want to provide a convenient way for users to send an email, directly from the webpage. When the link is activated, the browser should launch the default desktop application for handling email. You can think of this as a desktop-based protocol handler.
Web-based protocol handlers allow web-based applications to participate in the process too. This is becoming more important as more types of applications migrate to the web. In fact, there are many web-based email handling applications that could process a mailto link.
Registering
Setting up a web application as a protocol handler is not a difficult process. Basically, the web application uses registerProtocolHandler() to register itself with the browser as a potential handler for a given protocol. For example:
js
navigator.registerProtocolHandler(
"web+burger",
"http://www.google.co.uk/?uri=%s",
"Burger handler"
);
Where the parameters are:
- The protocol.
- The URL template, used as the handler. The "%s" is replaced with the
hrefof the link and a GET is executed on the resultant URL. - The user friendly name for the protocol handler.
When a browser executes this code, it should let the user choose how to handle the protocol. The browser could prompt the user for registration immediately, or wait until the user clicks on a link that uses the protocol. Firefox displays a prompt in the notification bar area:
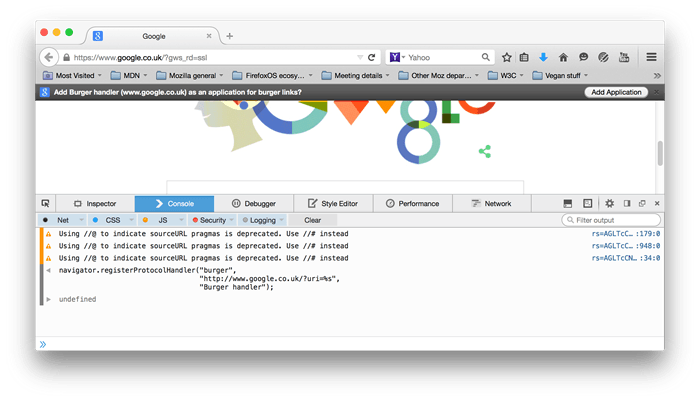
Note: The URL template supplied when registering must be of the same domain as the webpage attempting to perform the registration or the registration will fail. For example, http://example.com/homepage.html can register a protocol handler for http://example.com/handle_mailto/%s, but not for http://example.org/handle_mailto/%s.
Example
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Web Protocol Handler Sample - Register</title>
<script>
navigator.registerProtocolHandler(
"web+burger",
"http://www.google.co.uk/?uri=%s",
"Burger handler"
);
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Web Protocol Handler Sample</h1>
<p>
This web page will install a web protocol handler for the
<code>web+burger:</code> protocol.
</p>
</body>
</html>
Activating
Now, anytime the user activates a link that uses the registered protocol, the browser will route the action to the URL supplied when the web application registered. Firefox will, by default, prompt the user before handling off the action.
Example
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Web Protocol Handler Sample - Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hey have you seen <a href="web+burger:cheeseburger">this</a> before?</p>
</body>
</html>
Handling
The next phase is handling the action. The browser extracts the href from the activated link, combines it with the URL template supplied during handler registration and performs an HTTP GET on the URL. So, using the above examples, the browser would perform a GET on this URL:
http://www.google.co.uk/?uri=web+burger:cheeseburger
Server side code can extract the query string parameters and perform the desired action.
Note: The server side code is passed the entire contents of the href. This means the server side code will have to parse out the protocol from the data.
Example
php
<?php
$value = "";
if ( isset ( $_GET["value"] ) ) {
$value = $_GET["value"];
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Web Protocol Handler Sample</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Web Protocol Handler Sample - Handler</h1>
<p>This web page is called when handling a <code>web+burger:</code> protocol action. The data sent:</p>
<textarea>
<?php echo(htmlspecialchars($value, ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8')); ?>
</textarea>
</body>
</html>
References
See also
nsIProtocolHandler(XUL only)- RegisterProtocolHandler Enhancing the Federated Web at Mozilla Webdev
- Register a custom protocolHandler at web.dev.